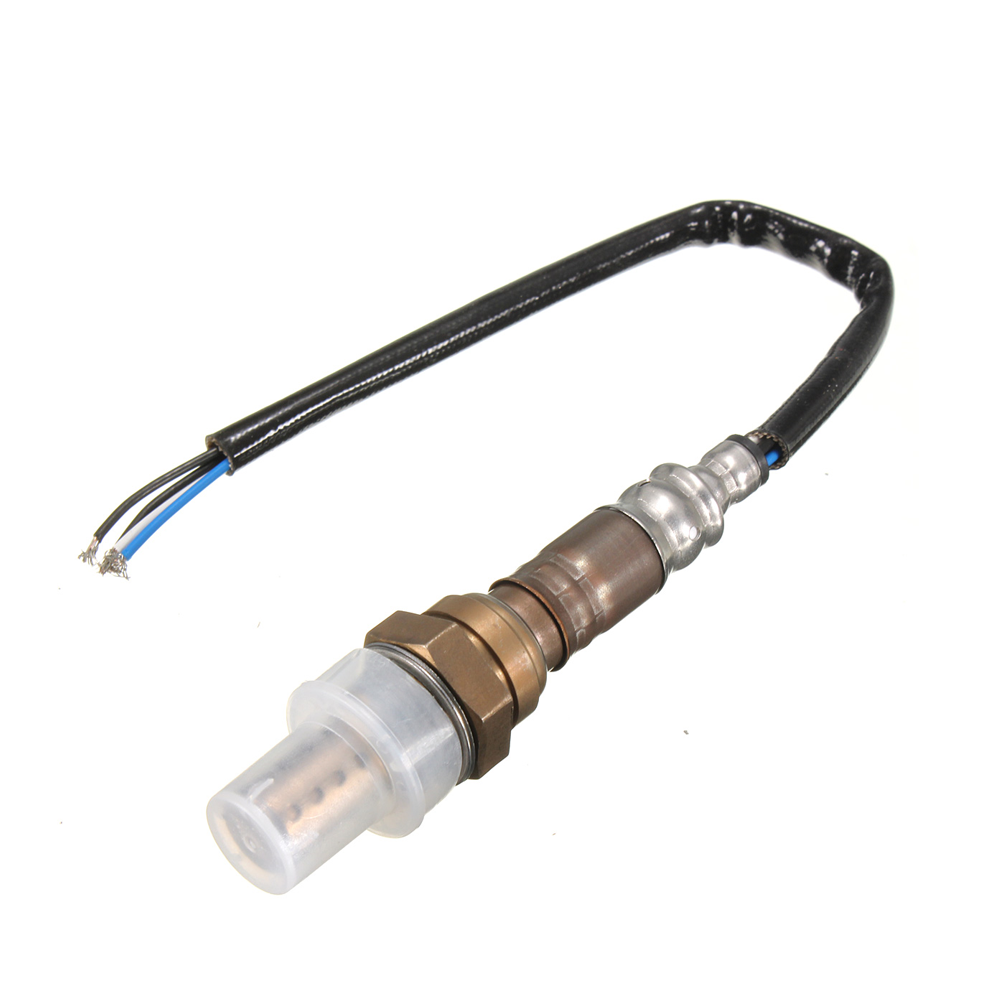
SENSORE Electronic offers two different types of oxygen sensors which are both based on zirconia oxide.
Because of the different physical properties either the amperometric oxygen sensor or the potentiometric oxygen sensor can be used depending on the application and operating environment
For all sensors types different housing designs are available depending on the application and the requirements.
Amperometric oxygen sensor
Amperometric oxygen sensors are characterized by the fact that the output signal of the sensor is an electrical current, which is defined by oxygen concentration of the environment.
The characteristic can thereby be represented as follows:
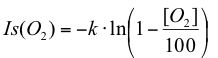
Is (O2) sensor current mA
[O2] oxygen concentration [%]
k sensorspecific constant
The oxygen sensor is characterized by very high accuracy and long life time.
Typical applications include medical applications (for example, oxygen concentrators), industry (e.g. protective gas processing), food and storage industry as well as measurement equipment.. Depending on the application for the optimal performance specific oxygen sensors are available with different measuring ranges.
For more details, please refer to the data sheet and further documentation in the download section.
Potentiometric oxygen sensor
Potentiometric oxygen sensors are characterized by the fact that the sensor signal is an electrical voltage, which is defined by ratio of partial pressures between measurement medium and a user-definable reference.
The characteristic can thereby be represented as follows:
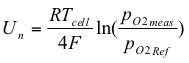
Un Cell voltage [V]
R Gas constant (8,314 J mol−1 K−1)
FFaraday constant ( 96485 C mol−1 )
TCell temperature [K]
pO2meas Measuring gas [mbar]
pO2Ref Reference gas [mbar]
This sensor is characterized by its robustness, humidity resistance and long life time.
Typical applications are automatic cooking either in home appliance or professional equipment. and food transport (container). For this sensor type there is only one measuring range available which covers all possible oxygen concentration ranges.
For more details, please refer to the data sheet and further documentation in the download section.